继上一篇文章Java集合框架综述后,今天正式开始分析具体集合类的代码,首先以既熟悉又陌生的HashMap开始。
本文源码分析基于Oracle JDK 1.7.0_71,请知悉。
$ java -version
java version "1.7.0_71"
Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.7.0_71-b14)
Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (build 24.71-b01, mixed mode)
签名(signature)
public class HashMap<K,V>
extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable
可以看到HashMap继承了
- 标记接口Cloneable,用于表明
HashMap对象会重写java.lang.Object#clone()方法,HashMap实现的是浅拷贝(shallow copy)。 - 标记接口Serializable,用于表明
HashMap对象可以被序列化
比较有意思的是,HashMap同时继承了抽象类AbstractMap与接口Map,因为抽象类AbstractMap的签名为
public abstract class AbstractMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V>
Stack Overfloooow上解释到:
在语法层面继承接口
Map是多余的,这么做仅仅是为了让阅读代码的人明确知道HashMap是属于Map体系的,起到了文档的作用
AbstractMap相当于个辅助类,Map的一些操作这里面已经提供了默认实现,后面具体的子类如果没有特殊行为,可直接使用AbstractMap提供的实现。
Cloneable接口
It's evil, don't use it.
Cloneable这个接口设计的非常不好,最致命的一点是它里面竟然没有clone方法,也就是说我们自己写的类完全可以实现这个接口的同时不重写clone方法。
关于Cloneable的不足,大家可以去看看《Effective Java》一书的作者给出的理由,在所给链接的文章里,Josh Bloch也会讲如何实现深拷贝比较好,我这里就不在赘述了。
Map接口
在eclipse中的outline面板可以看到Map接口里面包含以下成员方法与内部类:
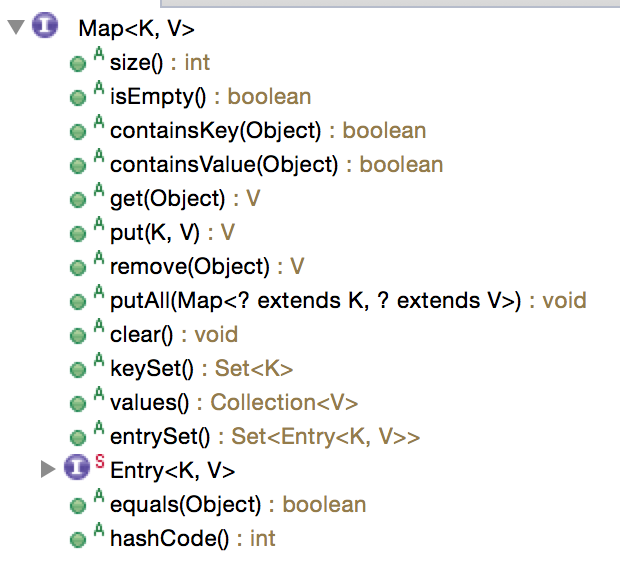
可以看到,这里的成员方法不外乎是“增删改查”,这也反映了我们编写程序时,一定是以“数据”为导向的。
在上篇文章讲了Map虽然并不是Collection,但是它提供了三种“集合视角”(collection views),与下面三个方法一一对应:
Set<K> keySet(),提供key的集合视角Collection<V> values(),提供value的集合视角Set<Map.Entry<K, V>> entrySet(),提供key-value序对的集合视角,这里用内部类Map.Entry表示序对
AbstractMap抽象类
AbstractMap对Map中的方法提供了一个基本实现,减少了实现Map接口的工作量。
举例来说:
如果要实现个不可变(unmodifiable)的map,那么只需继承
AbstractMap,然后实现其entrySet方法,这个方法返回的set不支持add与remove,同时这个set的迭代器(iterator)不支持remove操作即可。相反,如果要实现个可变(modifiable)的map,首先继承
AbstractMap,然后重写(override)AbstractMap的put方法,同时实现entrySet所返回set的迭代器的remove方法即可。
设计理念(design concept)
哈希表(hash table)
HashMap是一种基于哈希表(hash table)实现的map,哈希表(也叫关联数组)一种通用的数据结构,大多数的现代语言都原生支持,其概念也比较简单:key经过hash函数作用后得到一个槽(buckets或slots)的索引(index),槽中保存着我们想要获取的值,如下图所示
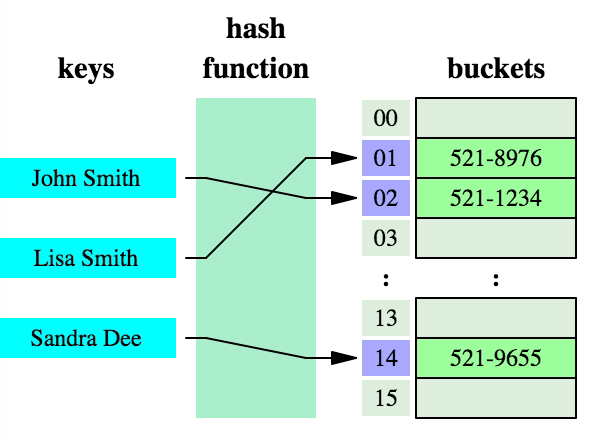
很容易想到,一些不同的key经过同一hash函数后可能产生相同的索引,也就是产生了冲突,这是在所难免的。 所以利用哈希表这种数据结构实现具体类时,需要:
- 设计个好的hash函数,使冲突尽可能的减少
- 其次是需要解决发生冲突后如何处理。
后面会重点介绍HashMap是如何解决这两个问题的。
HashMap的一些特点
- 线程非安全,并且允许key与value都为null值,
HashTable与之相反,为线程安全,key与value都不允许null值。 - 不保证其内部元素的顺序,而且随着时间的推移,同一元素的位置也可能改变(resize的情况)
- put、get操作的时间复杂度为O(1)。
- 遍历其集合视角的时间复杂度与其容量(capacity,槽的个数)和现有元素的大小(entry的个数)成正比,所以如果遍历的性能要求很高,不要把capactiy设置的过高或把平衡因子(load factor,当entry数大于capacity*loadFactor时,会进行resize,reside会导致key进行rehash)设置的过低。
- 由于HashMap是线程非安全的,这也就是意味着如果多个线程同时对一hashmap的集合试图做迭代时有结构的上改变(添加、删除entry,只改变entry的value的值不算结构改变),那么会报ConcurrentModificationException,专业术语叫
fail-fast,尽早报错对于多线程程序来说是很有必要的。 Map m = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap(...));通过这种方式可以得到一个线程安全的map。
源码剖析
首先从构造函数开始讲,HashMap遵循集合框架的约束,提供了一个参数为空的构造函数与有一个参数且参数类型为Map的构造函数。除此之外,还提供了两个构造函数,用于设置HashMap的容量(capacity)与平衡因子(loadFactor)。
1 public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
2 if (initialCapacity < 0)
3 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
4 initialCapacity);
5 if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
6 initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
7 if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
8 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
9 loadFactor);
10
11 this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
12 threshold = initialCapacity;
13 init();
14 }
15 public HashMap(int initialCapacity) {
16 this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
17 }
18 public HashMap() {
19 this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
20 }
从代码上可以看到,容量与平衡因子都有个默认值,并且容量有个最大值
1 /**
2 * The default initial capacity - MUST be a power of two.
3 */
4 static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16
5
6 /**
7 * The maximum capacity, used if a higher value is implicitly specified
8 * by either of the constructors with arguments.
9 * MUST be a power of two <= 1<<30.
10 */
11 static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
12
13 /**
14 * The load factor used when none specified in constructor.
15 */
16 static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
可以看到,默认的平衡因子为0.75,这是权衡了时间复杂度与空间复杂度之后的最好取值(JDK说是最好的😂),过高的因子会降低存储空间但是查找(lookup,包括HashMap中的put与get方法)的时间就会增加。
这里比较奇怪的是问题:容量必须为2的指数倍(默认为16),这是为什么呢?解答这个问题,需要了解HashMap中哈希函数的设计原理。
哈希函数的设计原理
1 /**
2 * Retrieve object hash code and applies a supplemental hash function to the
3 * result hash, which defends against poor quality hash functions. This is
4 * critical because HashMap uses power-of-two length hash tables, that
5 * otherwise encounter collisions for hashCodes that do not differ
6 * in lower bits. Note: Null keys always map to hash 0, thus index 0.
7 */
8 final int hash(Object k) {
9 int h = hashSeed;
10 if (0 != h && k instanceof String) {
11 return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k);
12 }
13
14 h ^= k.hashCode();
15
16 // This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by
17 // constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded
18 // number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor).
19 h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
20 return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
21 }
22
23 /**
24 * Returns index for hash code h.
25 */
26 static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
27 // assert Integer.bitCount(length) == 1 : "length must be a non-zero power of 2";
28 return h & (length-1);
29 }
看到这么多位操作,是不是觉得晕头转向了呢,还是搞清楚原理就行了,毕竟位操作速度是很快的,不能因为不好理解就不用了😊。 网上说这个问题的也比较多,我这里根据自己的理解,尽量做到通俗易懂。
在哈希表容量(也就是buckets或slots大小)为length的情况下,为了使每个key都能在冲突最小的情况下映射到[0,length)(注意是左闭右开区间)的索引(index)内,一般有两种做法:
- 让length为素数,然后用
hashCode(key) mod length的方法得到索引 - 让length为2的指数倍,然后用
hashCode(key) & (length-1)的方法得到索引
HashTable用的是方法1,HashMap用的是方法2。
因为本篇主题讲的是HashMap,所以关于方法1为什么要用素数,我这里不想过多介绍,大家可以看这里。
重点说说方法2的情况,方法2其实也比较好理解:
因为length为2的指数倍,所以
length-1所对应的二进制位都为1,然后在与hashCode(key)做与运算,即可得到[0,length)内的索引
但是这里有个问题,如果hashCode(key)的大于length的值,而且hashCode(key)的二进制位的低位变化不大,那么冲突就会很多,举个例子:
Java中对象的哈希值都32位整数,而HashMap默认大小为16,那么有两个对象那么的哈希值分别为:
0xABAB0000与0xBABA0000,它们的后几位都是一样,那么与16异或后得到结果应该也是一样的,也就是产生了冲突。
造成冲突的原因关键在于16限制了只能用低位来计算,高位直接舍弃了,所以我们需要额外的哈希函数而不只是简单的对象的hashCode方法了。
具体来说,就是HashMap中hash函数干的事了
首先有个随机的hashSeed,来降低冲突发生的几率
然后如果是字符串,用了
sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k);来获取索引值最后,通过一系列无符号右移操作,来把高位与低位进行异或操作,来降低冲突发生的几率
右移的偏移量20,12,7,4是怎么来的呢?因为Java中对象的哈希值都是32位的,所以这几个数应该就是把高位与低位做异或运算,至于这几个数是如何选取的,就不清楚了,网上搜了半天也没统一且让人信服的说法,大家可以参考下面几个链接:
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/7922019/openjdks-rehashing-mechanism/7922219#7922219
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/9335169/understanding-strange-java-hash-function/9336103#9336103
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/14453163/can-anybody-explain-how-java-design-hashmaps-hash-function/14479945#14479945
HashMap.Entry
HashMap中存放的是HashMap.Entry对象,它继承自Map.Entry,其比较重要的是构造函数
1 static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
2 final K key;
3 V value;
4 Entry<K,V> next;
5 int hash;
6
7 Entry(int h, K k, V v, Entry<K,V> n) {
8 value = v;
9 next = n;
10 key = k;
11 hash = h;
12 }
13 // setter, getter, equals, toString 方法省略
14 public final int hashCode() {
15 //用key的hash值与上value的hash值作为Entry的hash值
16 return Objects.hashCode(getKey()) ^ Objects.hashCode(getValue());
17 }
18 /**
19 * This method is invoked whenever the value in an entry is
20 * overwritten by an invocation of put(k,v) for a key k that's already
21 * in the HashMap.
22 */
23 void recordAccess(HashMap<K,V> m) {
24 }
25
26 /**
27 * This method is invoked whenever the entry is
28 * removed from the table.
29 */
30 void recordRemoval(HashMap<K,V> m) {
31 }
32 }
可以看到,Entry实现了单向链表的功能,用next成员变量来级连起来。
介绍完Entry对象,下面要说一个比较重要的成员变量
/**
* The table, resized as necessary. Length MUST Always be a power of two.
*/
//HashMap内部维护了一个为数组类型的Entry变量table,用来保存添加进来的Entry对象
transient Entry<K,V>[] table = (Entry<K,V>[]) EMPTY_TABLE;
你也许会疑问,Entry不是单向链表嘛,怎么这里又需要个数组类型的table呢? 我翻了下之前的算法书,其实这是解决冲突的一个方式:链地址法(开散列法),效果如下:
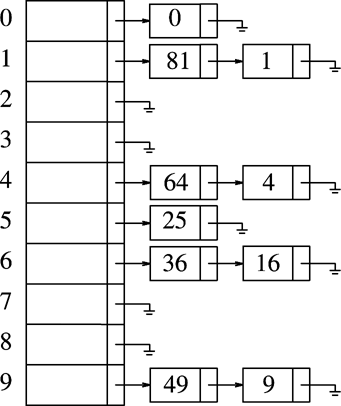
链地址法的可视化
网上找到个很好的网站,用来可视化各种常见的算法,很棒。瞬间觉得国外大学比国内的强不知多少倍。 下面的链接可以模仿哈希表采用链地址法解决冲突,大家可以自己去玩玩😊
get操作
get操作相比put操作简单,所以先介绍get操作
1 public V get(Object key) {
2 //单独处理key为null的情况
3 if (key == null)
4 return getForNullKey();
5 Entry<K,V> entry = getEntry(key);
6
7 return null == entry ? null : entry.getValue();
8 }
9 private V getForNullKey() {
10 if (size == 0) {
11 return null;
12 }
13 //key为null的Entry用于放在table[0]中,但是在table[0]冲突链中的Entry的key不一定为null
14 //所以需要遍历冲突链,查找key是否存在
15 for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) {
16 if (e.key == null)
17 return e.value;
18 }
19 return null;
20 }
21 final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
22 if (size == 0) {
23 return null;
24 }
25
26 int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key);
27 //首先定位到索引在table中的位置
28 //然后遍历冲突链,查找key是否存在
29 for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)];
30 e != null;
31 e = e.next) {
32 Object k;
33 if (e.hash == hash &&
34 ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
35 return e;
36 }
37 return null;
38 }
put操作(含update操作)
因为put操作有可能需要对HashMap进行resize,所以实现略复杂些
1 private void inflateTable(int toSize) {
2 //辅助函数,用于填充HashMap到指定的capacity
3 // Find a power of 2 >= toSize
4 int capacity = roundUpToPowerOf2(toSize);
5 //threshold为resize的阈值,超过后HashMap会进行resize,内容的entry会进行rehash
6 threshold = (int) Math.min(capacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
7 table = new Entry[capacity];
8 initHashSeedAsNeeded(capacity);
9 }
10 /**
11 * Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map.
12 * If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old
13 * value is replaced.
14 */
15 public V put(K key, V value) {
16 if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {
17 inflateTable(threshold);
18 }
19 if (key == null)
20 return putForNullKey(value);
21 int hash = hash(key);
22 int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
23 //这里的循环是关键
24 //当新增的key所对应的索引i,对应table[i]中已经有值时,进入循环体
25 for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
26 Object k;
27 //判断是否存在本次插入的key,如果存在用本次的value替换之前oldValue,相当于update操作
28 //并返回之前的oldValue
29 if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
30 V oldValue = e.value;
31 e.value = value;
32 e.recordAccess(this);
33 return oldValue;
34 }
35 }
36 //如果本次新增key之前不存在于HashMap中,modCount加1,说明结构改变了
37 modCount++;
38 addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
39 return null;
40 }
41 void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
42 //如果增加一个元素会后,HashMap的大小超过阈值,需要resize
43 if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
44 //增加的幅度是之前的1倍
45 resize(2 * table.length);
46 hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;
47 bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);
48 }
49
50 createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
51 }
52 void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
53 //首先得到该索引处的冲突链Entries,第一次插入bucketIndex位置时冲突链为null,也就是e为null
54 Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
55 //然后把新的Entry添加到冲突链的开头,也就是说,后插入的反而在前面(第一次还真没看明白)
56 //table[bucketIndex]为新加入的Entry,是bucketIndex位置的冲突链的第一个元素
57 table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
58 size++;
59 }
60 //下面看看HashMap是如何进行resize,庐山真面目就要揭晓了😊
61 void resize(int newCapacity) {
62 Entry[] oldTable = table;
63 int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
64 //如果已经达到最大容量,那么就直接返回
65 if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
66 threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
67 return;
68 }
69
70 Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
71 //initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity)的返回值决定了是否需要重新计算Entry的hash值
72 transfer(newTable, initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity));
73 table = newTable;
74 threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
75 }
76
77 /**
78 * Transfers all entries from current table to newTable.
79 */
80 void transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) {
81 int newCapacity = newTable.length;
82 //遍历当前的table,将里面的元素添加到新的newTable中
83 for (Entry<K,V> e : table) {
84 while(null != e) {
85 Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
86 if (rehash) {
87 e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key);
88 }
89 int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);
90 e.next = newTable[i];
91 //最后这两句用了与put放过相同的技巧
92 //将后插入的反而在前面
93 newTable[i] = e;
94 e = next;
95 }
96 }
97 }
98 /**
99 * Initialize the hashing mask value. We defer initialization until we
100 * really need it.
101 */
102 final boolean initHashSeedAsNeeded(int capacity) {
103 boolean currentAltHashing = hashSeed != 0;
104 boolean useAltHashing = sun.misc.VM.isBooted() &&
105 (capacity >= Holder.ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD);
106 //这里说明了,在hashSeed不为0或满足useAltHash时,会重算Entry的hash值
107 //至于useAltHashing的作用可以参考下面的链接
108 // http://stackoverflow.com/questions/29918624/what-is-the-use-of-holder-class-in-hashmap
109 boolean switching = currentAltHashing ^ useAltHashing;
110 if (switching) {
111 hashSeed = useAltHashing
112 ? sun.misc.Hashing.randomHashSeed(this)
113 : 0;
114 }
115 return switching;
116 }
remove操作
1 public V remove(Object key) {
2 Entry<K,V> e = removeEntryForKey(key);
3 //可以看到删除的key如果存在,就返回其所对应的value
4 return (e == null ? null : e.value);
5 }
6 final Entry<K,V> removeEntryForKey(Object key) {
7 if (size == 0) {
8 return null;
9 }
10 int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key);
11 int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
12 //这里用了两个Entry对象,相当于两个指针,为的是防治冲突链发生断裂的情况
13 //这里的思路就是一般的单向链表的删除思路
14 Entry<K,V> prev = table[i];
15 Entry<K,V> e = prev;
16
17 //当table[i]中存在冲突链时,开始遍历里面的元素
18 while (e != null) {
19 Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
20 Object k;
21 if (e.hash == hash &&
22 ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
23 modCount++;
24 size--;
25 if (prev == e) //当冲突链只有一个Entry时
26 table[i] = next;
27 else
28 prev.next = next;
29 e.recordRemoval(this);
30 return e;
31 }
32 prev = e;
33 e = next;
34 }
35
36 return e;
37 }
到现在为止,HashMap的增删改查都介绍完了。 一般而言,认为HashMap的这四种操作时间复杂度为O(1),因为它hash函数性质较好,保证了冲突发生的几率较小。
fast-fail的HashIterator
集合类用Iterator类来遍历其包含的元素,接口Enumeration已经不推荐使用。相比Enumeration,Iterator有下面两个优势:
- Iterator允许调用者在遍历集合类时删除集合类中包含的元素(相比Enumeration增加了remove方法)
- 比Enumeration的命名更简短
HashMap中提供的三种集合视角,底层都是用HashIterator实现的。
1 private abstract class HashIterator<E> implements Iterator<E> {
2 Entry<K,V> next; // next entry to return
3 //在初始化Iterator实例时,纪录下当前的修改次数
4 int expectedModCount; // For fast-fail
5 int index; // current slot
6 Entry<K,V> current; // current entry
7
8 HashIterator() {
9 expectedModCount = modCount;
10 if (size > 0) { // advance to first entry
11 Entry[] t = table;
12 //遍历HashMap的table,依次查找元素
13 while (index < t.length && (next = t[index++]) == null)
14 ;
15 }
16 }
17
18 public final boolean hasNext() {
19 return next != null;
20 }
21
22 final Entry<K,V> nextEntry() {
23 //在访问下一个Entry时,判断是否有其他线程有对集合的修改
24 //说明HashMap是线程非安全的
25 if (modCount != expectedModCount)
26 throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
27 Entry<K,V> e = next;
28 if (e == null)
29 throw new NoSuchElementException();
30
31 if ((next = e.next) == null) {
32 Entry[] t = table;
33 while (index < t.length && (next = t[index++]) == null)
34 ;
35 }
36 current = e;
37 return e;
38 }
39
40 public void remove() {
41 if (current == null)
42 throw new IllegalStateException();
43 if (modCount != expectedModCount)
44 throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
45 Object k = current.key;
46 current = null;
47 HashMap.this.removeEntryForKey(k);
48 expectedModCount = modCount;
49 }
50 }
51
52 private final class ValueIterator extends HashIterator<V> {
53 public V next() {
54 return nextEntry().value;
55 }
56 }
57
58 private final class KeyIterator extends HashIterator<K> {
59 public K next() {
60 return nextEntry().getKey();
61 }
62 }
63
64 private final class EntryIterator extends HashIterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
65 public Map.Entry<K,V> next() {
66 return nextEntry();
67 }
68 }
序列化
介绍到这里,基本上算是把HashMap中一些核心的点讲完了,但还有个比较严重的问题:保存Entry的table数组为transient的,也就是说在进行序列化时,并不会包含该成员,这是为什么呢?
transient Entry<K,V>[] table = (Entry<K,V>[]) EMPTY_TABLE;
为了解答这个问题,我们需要明确下面事实:
- Object.hashCode方法对于一个类的两个实例返回的是不同的哈希值
我们可以试想下面的场景:
我们在机器A上算出对象A的哈希值与索引,然后把它插入到HashMap中,然后把该HashMap序列化后,在机器B上重新算对象的哈希值与索引,这与机器A上算出的是不一样的,所以我们在机器B上get对象A时,会得到错误的结果。
所以说,当序列化一个HashMap对象时,保存Entry的table是不需要序列化进来的,因为它在另一台机器上是错误的。
因为这个原因,HashMap重写了writeObject与readObject 方法
1private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
2 throws IOException
3{
4 // Write out the threshold, loadfactor, and any hidden stuff
5 s.defaultWriteObject();
6
7 // Write out number of buckets
8 if (table==EMPTY_TABLE) {
9 s.writeInt(roundUpToPowerOf2(threshold));
10 } else {
11 s.writeInt(table.length);
12 }
13
14 // Write out size (number of Mappings)
15 s.writeInt(size);
16
17 // Write out keys and values (alternating)
18 if (size > 0) {
19 for(Map.Entry<K,V> e : entrySet0()) {
20 s.writeObject(e.getKey());
21 s.writeObject(e.getValue());
22 }
23 }
24}
25
26private static final long serialVersionUID = 362498820763181265L;
27
28private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
29 throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException
30{
31 // Read in the threshold (ignored), loadfactor, and any hidden stuff
32 s.defaultReadObject();
33 if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) {
34 throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal load factor: " +
35 loadFactor);
36 }
37
38 // set other fields that need values
39 table = (Entry<K,V>[]) EMPTY_TABLE;
40
41 // Read in number of buckets
42 s.readInt(); // ignored.
43
44 // Read number of mappings
45 int mappings = s.readInt();
46 if (mappings < 0)
47 throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal mappings count: " +
48 mappings);
49
50 // capacity chosen by number of mappings and desired load (if >= 0.25)
51 int capacity = (int) Math.min(
52 mappings * Math.min(1 / loadFactor, 4.0f),
53 // we have limits...
54 HashMap.MAXIMUM_CAPACITY);
55
56 // allocate the bucket array;
57 if (mappings > 0) {
58 inflateTable(capacity);
59 } else {
60 threshold = capacity;
61 }
62
63 init(); // Give subclass a chance to do its thing.
64
65 // Read the keys and values, and put the mappings in the HashMap
66 for (int i = 0; i < mappings; i++) {
67 K key = (K) s.readObject();
68 V value = (V) s.readObject();
69 putForCreate(key, value);
70 }
71}
72private void putForCreate(K key, V value) {
73 int hash = null == key ? 0 : hash(key);
74 int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
75
76 /**
77 * Look for preexisting entry for key. This will never happen for
78 * clone or deserialize. It will only happen for construction if the
79 * input Map is a sorted map whose ordering is inconsistent w/ equals.
80 */
81 for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
82 Object k;
83 if (e.hash == hash &&
84 ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
85 e.value = value;
86 return;
87 }
88 }
89
90 createEntry(hash, key, value, i);
91}
简单来说,在序列化时,针对Entry的key与value分别单独序列化,当反序列化时,再单独处理即可。
总结
在总结完HashMap后,发现这里面一些核心的东西,像哈希表的冲突解决,都是算法课上学到,不过由于“年代久远”,已经忘得差不多了,我觉得忘
- 一方面是由于时间久不用
- 另一方面是由于本身没理解好
平时多去思考,这样在遇到一些性能问题时也好排查。
还有一点就是我们在分析某些具体类或方法时,不要花太多时间一些细枝末节的边界条件上,这样很得不偿失,倒不是说这么边界条件不重要,程序的bug往往就是边界条件没考虑周全导致的。 只是说我们可以在理解了这个类或方法的总体思路后,再来分析这些边界条件。 如果一开始就分析,那真是丈二和尚——摸不着头脑了,随着对它工作原理的加深,才有可能理解这些边界条件的场景。
今天到此为止,下次打算分析TreeMap。Stay Tuned!🍺。我已经写完了,两篇文章对比看,效果更好。